Connecting Java API Backend with a Simple Web Frontend [Part-3]
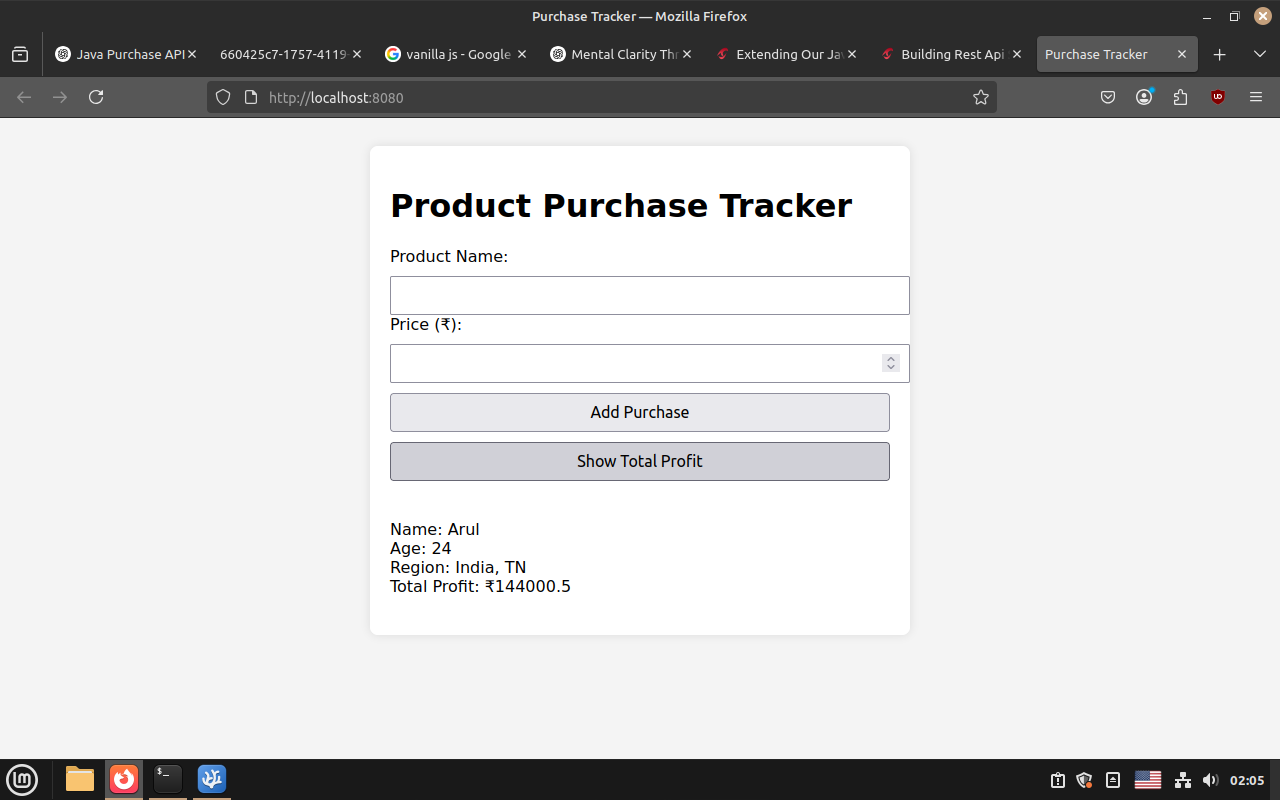
Show Total:
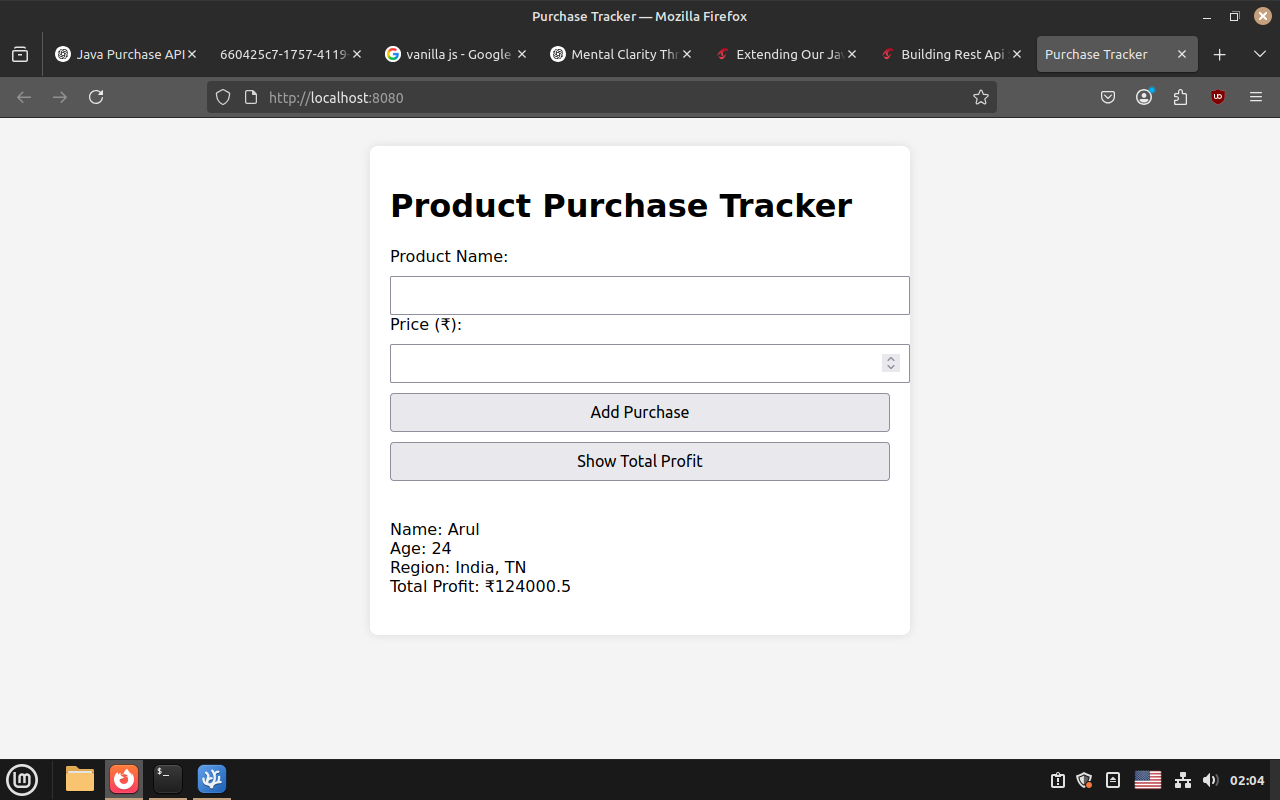
Purchasing product:
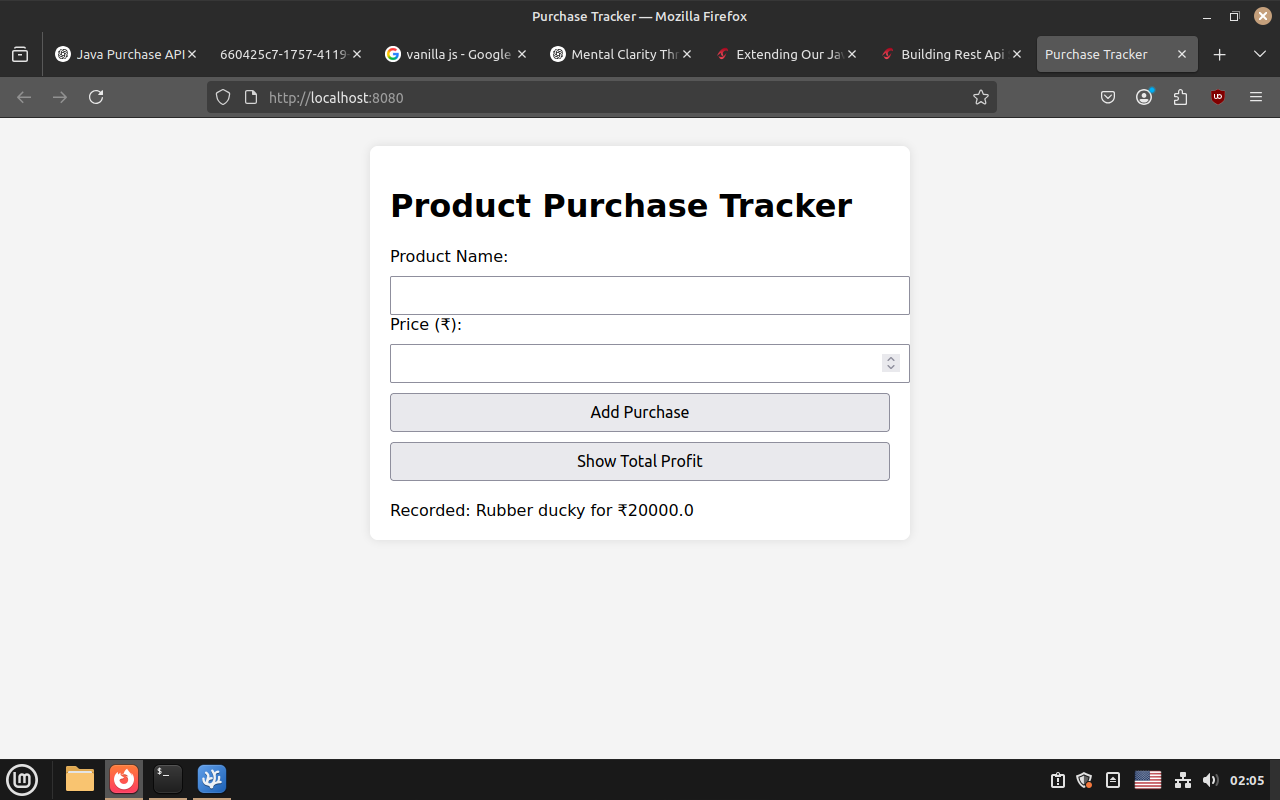
Final Total:
We’ve created a clean and functional REST API backend using Java + Javalin, paired with a vanilla HTML + JS frontend — no frameworks, no fuss.
This post walks through how the two sides talk to each other and explains critical bits like CORS, fetch(), and arrow functions (=>). Simple, clean, and beginner-friendly.
🔌 Project Overview
java-project/
├── App.java ← REST API (Javalin)
├── Constructor.java ← Holds customer info
├── PurchaseDAO.java ← SQLite DB access
└── frontend/
├── index.html ← HTML Form UI
├── app.js ← JS to call backend
└── styles.css ← Basic styling
🗃️ Java Backend Code (Reference Only)
These are the backend files from previous parts. If you’re new, start with:
- 👉 Part 1: ️Building Rest Api Server from scratch using Java and Javalin
- 👉 Part 2: Extending Our Java REST API: Now with SQLite for Persistent Storage
Feel free to browse the full source here:
package com.test;
//Custom Classes Imported below
import com.test.PurchaseDAO;
// Import necessary classes
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Scanner;
import io.javalin.Javalin;
import io.javalin.http.Context;
import io.javalin.plugin.bundled.CorsPluginConfig;
public class App {
// Create a Constructor object to hold user and product info
Constructor construct = new Constructor("Arul", 24, "India, TN");
// Counter to track number of products purchased
int productIndex = 0;
// Map to store product name as key and price as value
Map<String, Double> purchasedProductDetails = new HashMap<>();
// Scanner object to read input from console
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
PurchaseDAO db = new PurchaseDAO(); // Initializing DB
// Method to record a purchase
public void recordPurchase(String product, double price) {
productIndex++; // Increment product count
construct.setProductName(product); // Set product name
construct.setProductPrice(price); // Set product price
construct.setTotalProductsPurchased(productIndex); // Update total
makeList(); // Add to local Map
db.insertPurchase(product, price); // Save to DB
}
// Read user input from console (for CLI use)
public void printAndRead() {
System.out.println("[+] Enter the Product " + productIndex + " Name:");
String productName = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("[+] Enter price of the Product");
Double productPrice = scanner.nextDouble();
scanner.nextLine(); // Consume newline
recordPurchase(productName, productPrice);
}
// Add product and price to Map
public void makeList() {
purchasedProductDetails.put(construct.getProductName(), construct.getProductPrice());
}
// Calculate total from DB and print
public void calculateTotalProfit() {
double sum = db.getTotalProfit(); // From DB
System.out.println("Total profit: ₹" + sum);
}
// Start API server
public void startApi() {
Javalin app = Javalin.create(config -> {
// Enable CORS for frontend origin
config.plugins.enableCors(cors -> {
cors.add(CorsPluginConfig::anyHost); // Or use allowHost("http://localhost:8080")
});
}).start(7070);
// Set JSON response type
app.before(ctx -> ctx.contentType("application/json"));
// POST /purchase → Record purchase
app.post("/purchase", ctx -> {
Map<String, Object> data = ctx.bodyAsClass(Map.class);
String product = data.get("product").toString();
double price = Double.parseDouble(data.get("price").toString());
recordPurchase(product, price);
ctx.status(200).result("Recorded: " + product + " for ₹" + price);
});
// GET /total → Return total profit
app.get("/total", ctx -> {
double sum = db.getTotalProfit();
ctx.json(Map.of(
"totalProfit", sum,
"customerName", construct.name,
"customerAge", construct.age,
"customerRegion", construct.region
));
});
}
// Main Method
public static void main(String[] args) {
App app = new App();
app.startApi(); // Start server
// Optional CLI (not needed for frontend, just for manual entry)
int flag = 0;
while (flag != 1) {
System.out.println("Proceed Adding Products? (Y/N)");
String userInput = app.scanner.nextLine();
if (userInput.equalsIgnoreCase("Y")) {
app.printAndRead();
} else {
app.calculateTotalProfit();
flag = 1;
app.scanner.close();
}
}
}
}
package com.test;
public class Constructor {
// User info fields
String name;
int age;
String region;
// Product-related fields (private for encapsulation)
private String purchaseProduct;
private double productPrice;
private double profitOfTheDay;
private int totalProductsPurchased;
// Constructor to initialize user details
public Constructor(String name, int age, String region) {
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
this.region = region;
}
// Getter for product name
public String getProductName() {
return purchaseProduct;
}
// Getter for product price
public double getProductPrice() {
return productPrice;
}
// Getter for profit of the day (not used yet in App)
public double getProfitOfTheDay() {
return profitOfTheDay;
}
// Setter for product name
public void setProductName(String purchaseProduct) {
this.purchaseProduct = purchaseProduct;
}
// Setter for product price
public void setProductPrice(double productPrice) {
this.productPrice = productPrice;
}
// Setter for profit of the day
public void setProfitOfTheDay(double profitOfTheDay) {
this.profitOfTheDay = profitOfTheDay;
}
// Setter for total products purchased
public void setTotalProductsPurchased(int totalProductsPurchased) {
this.totalProductsPurchased = totalProductsPurchased;
}
// Getter for total products purchased
public int getTotalProductsPurchased() {
return totalProductsPurchased;
}
}
package com.test;
import java.sql.*;
public class PurchaseDAO {
private static final String DB_URL = "jdbc:sqlite:purchase.db";
public PurchaseDAO(){
try(Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL);
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement())
{
String sql = "CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS purchases ("
+ "id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,"
+ "product TEXT NOT NULL,"
+ "price REAL NOT NULL);";
stmt.execute(sql);
}
catch(SQLException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void insertPurchase(String product, double price){
String sql = "INSERT INTO purchases (product, price) VALUES (?,?)";
try (Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL);
PreparedStatement pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql)){
pstmt.setString(1, product);
pstmt.setDouble(2, price);
pstmt.executeUpdate();
}
catch(SQLException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public double getTotalProfit(){
double total = 0;
String sql = "SELECT SUM(price) FROM purchases";
try(Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL);
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
ResultSet res = stmt.executeQuery(sql)){
if(res.next()){
total = res.getDouble(1);
}
}
catch(SQLException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return total;
}
}
🛠️ Enabled CORS in Java Backend API (Javalin)
Javalin app = Javalin.create(config -> {
config.plugins.enableCors(cors -> {
cors.add(CorsPluginConfig::anyHost); // Allow all origins (dev only)
});
}).start(7070);
🔐 What is CORS?
By default, browsers block JS running on one origin (e.g., localhost:8080) from talking to an API on another (e.g., localhost:7070). This is called Cross-Origin Request Blocking.
✅ To allow the frontend to talk to the backend:
- We enable CORS using
config.plugins.enableCors(...). - For local testing,
anyHostis fine. - In production, always restrict to specific domains.
🖥️ Frontend Code
Let’s break down each part of the frontend.
✅ index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Purchase Tracker</title>
<!-- Link CSS -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="styles.css" />
<!-- Link JS (corrected attribute typo: 'data-jslicence' to 'data-jslicense') -->
<script src="app.js" defer data-jslicense="MIT"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<h1>Product Purchase Tracker</h1>
<!-- Purchase form -->
<form id="purchaseForm">
<label for="product">Product Name:</label>
<input type="text" id="product" name="product" required />
<label for="price">Price (₹):</label>
<input type="number" id="price" name="price" step="0.01" required />
<button type="submit">Add Purchase</button>
</form>
<!-- Button to fetch total -->
<button id="totalBtn">Show Total Profit</button>
<!-- Result will be shown here -->
<div id="result"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
🧠 How This Page Talks to Backend
- A form collects
productandprice. - JavaScript catches the form submission and sends a
POSTrequest to your API. - The API records it in SQLite.
- You can click another button to send a
GETrequest to show total profit. - All this is rendered inside the
#resultdiv.
🧠 app.js
// Wait until the DOM (HTML page) is fully loaded
document.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded", function () {
// Grab form elements and buttons
const form = document.getElementById("purchaseForm");
const resultDiv = document.getElementById("result");
const totalBtn = document.getElementById("totalBtn");
// Handle form submission (Add new Purchase)
form.addEventListener("submit", function (event) {
event.preventDefault(); // Prevent page refresh
// Get product and price values from form
const product = document.getElementById("product").value;
const price = parseFloat(document.getElementById("price").value);
const data = { product: product, price: price };
// Send POST request to /purchase endpoint
fetch("http://localhost:7070/purchase", {
method: "POST",
headers: { "Content-Type": "application/json" },
body: JSON.stringify(data),
})
.then(function (response) {
return response.text(); // Expecting plain text response
})
.then(function (data) {
resultDiv.innerText = data; // Show server response
form.reset(); // Clear form inputs
})
.catch(function (error) {
resultDiv.innerText = "Error: " + error; // Show error if any
});
});
// Handle "Show Total Profit" button click (GET from /total)
totalBtn.addEventListener("click", function () {
fetch("http://localhost:7070/total")
.then((response) => response.json()) // Expect JSON response
.then((data) => {
// Format and display returned data
const output = `
Name: ${data.customerName}
Age: ${data.customerAge}
Region: ${data.customerRegion}
Total Profit: ₹${data.totalProfit}
`;
resultDiv.innerText = output;
})
.catch((error) => {
resultDiv.innerText = "Error: " + error; // Display fetch error
});
});
});
⚙️ How JavaScript Interacts with Your Java API
-
When form is submitted:
- It sends a
POSTrequest to:http://localhost:7070/purchase - The Java server reads the body using:
ctx.bodyAsClass(Map.class) - It responds with:
"Recorded: Laptop for ₹45000"
- It sends a
-
When “Show Total” button is clicked:
- It sends a
GETrequest to:http://localhost:7070/total - Java API responds with a JSON:
- It sends a
{
"customerName": "Arul",
"totalProfit": 75000.5,
"customerRegion": "India, TN",
"customerAge": 24
}
- JS displays this in
#result.
🔁 About the => Arrow Function
This is modern JavaScript syntax to define functions:
.then((data) => {
console.log(data);
})
⬆️ Same as:
.then(function(data) {
console.log(data);
})
Arrow functions are shorter and preserve the this context.
🎨 styles.css
body {
font-family: sans-serif;
background-color: #f4f4f4;
padding: 20px;
}
.container {
max-width: 500px;
margin: auto;
background: white;
padding: 20px;
border-radius: 8px;
box-shadow: 0 0 10px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1); /* optional visual polish */
}
input,
button {
display: block;
width: 100%;
margin-top: 10px;
padding: 8px;
font-size: 1rem;
}
#result {
margin-top: 20px;
white-space: pre-wrap; /* keep newlines and wrap long lines */
}
🎨 CSS Breakdown
| Selector | What it Targets | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
body |
Whole webpage | Applies a clean sans-serif font, sets light-gray background and padding for spacing. |
.container |
The main box around the form and results | Creates a centered white card with padding, rounded corners, and a soft drop shadow to make it visually appealing. |
input, button |
All input fields and buttons | Makes them full width, evenly padded, and consistent in size—ensures good mobile and desktop layout. |
#result |
The output display for responses | Adds top margin and white-space: pre-wrap so that multi-line text (like API JSON) is displayed clearly and wrapped properly. |
🌐 check my repo:
Uploaded this project in below repo link:
✅ That’s it
You’ve now connected a pure HTML/JS frontend to a Java API backend — no React, no JSP, no extra tools.
See you with another Interesting post, Untill then, happy coding. 🚀